
Grains are the edible seeds of plants that belong to the grass family. These would include wheat, rice, rye, barley, and millet, as well as others we often classify as "grain-like" such as buckwheat and quinoa which do not belong to the grass family.
This food group includes any foods made from the ingredients above, for example, bread, cereal, tortillas, and pasta.
Grains provide a significant amount of carbohydrates, acting as a great source of energy for the body.
Please note: This post contains affiliate links.
Different Kinds of Grains
Grains are further divided into two sub-groups: whole and refined.
Whole grains contain the entire grain kernel, while refined grains have had the bran and germ removed – this is how we get "white" flour, pasta, bread, etc. By this process, fiber, vitamins, and minerals are also removed from, so you'll always get more micronutrients by choosing whole grains.
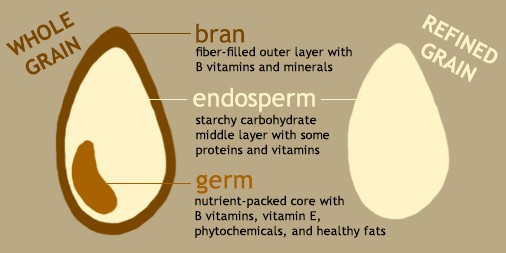
Whole grains contain important nutrients like dietary fiber, magnesium, iron, zinc, B vitamins, and vitamin E. They are a significant source of carbohydrates, and also contain a number of essential amino acids.
Daily Requirements
Daily requirements change rapidly between birth and 2 years of age, so we recommend you check out the age-specific meal plans for those ages.
| Age (years) | Men | Women |
| 2 - 3 | 3 oz equivalent | 3 oz equivalent |
| 4 - 8 | 5 oz equivalent | 5 oz equivalent |
| 9 - 13 | 6 oz equivalent | 5 oz equivalent |
| 14 - 18 | 8 oz equivalent | 6 oz equivalent |
| 19 - 30 | 8 oz equivalent | 6 oz equivalent |
| 31 - 50 | 7 oz equivalent | 6 oz equivalent |
| 51+ | 6 oz equivalent | 5 oz equivalent |
Portion Sizes
Check this out for a reference guide for how much of specific grains is meant by "1 oz equivalent".
